| IUPAC-recommended ring-lettering (left) and atom-numbering (right) ofcholestane, a prototypical steroid skeleton. The four rings A-D form the gonanenucleus of the steroid. |
| Stick model of the steroid lanosterol. The total number of carbons (30) reflects its triterpenoid origin. |
Structure:
Steroids are a class of organic compounds with a chemical structure that contains the core of gonane or a skeleton derived therefrom. Usually, methyl groups are present at the carbons C-10 and C-13 – an alkyl side-chain at carbon C-17 may also be present.
| Cholesterol. This steroid is the precursor to other steroidsin the steroidogenesis. |
| The basic skeleton of a steroid, with standard stereo orientation. R is a side-chain at C-17. |
Steroids
are a class of organic compounds with a chemical structure
that contains the core of gonane or a skeleton derived
therefrom. Usually, methyl groups are present at the
carbons C-10 and C-13 – an alkyl side-chain at
carbon C-17 may also be present.
Gonane is
the simplest possible steroid and is composed of
seventeen carbon atoms, bonded together to form four fused
rings. The three cyclohexane rings (designated as rings A,
B, and C in the figure below) form the skeleton of phenanthrene;
ring D has acyclopentane structure. Hence, together they are
called cyclopentaphenanthrene.
Commonly,
steroids have a methyl group at the carbons C-10 and C-13 and an
alkyl side chain at carbon C-17. Further, they vary by the
configuration of the side chain, the number of additional methyl
groups, and the functional groups attached to the rings. For
example, sterols have
a hydroxyl
group attached
at position C-3.
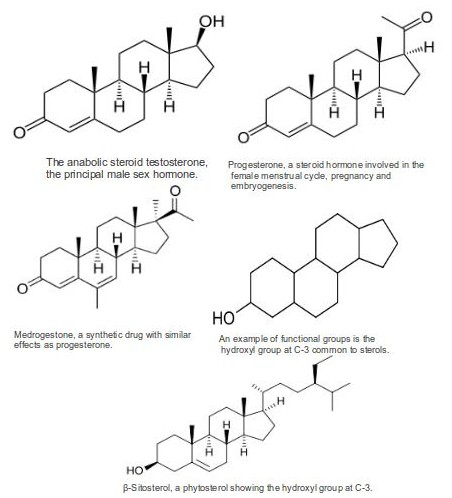
Some
exemplary steroids with their structures:
Classification:
Taxonomical/Functional
Some
of the common categories of steroids:
- Animal
- Insect
- Ecdysteroids such as ecdysterone
- Vertebrate
- Steroid hormones
- Sex steroids are a subset of sex hormones that produce sex differences or support reproduction. They include androgens,estrogens, and progestagens.
- Corticosteroids include glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids. Glucocorticoids regulate many aspects of metabolism andimmune function, whereas mineralocorticoids help maintain blood volume and control renal excretion of electrolytes. Most medical 'steroid' drugs are corticosteroids.
- Anabolic steroids are a class of steroids that interact with androgen receptors to increase muscle and bone synthesis. There are natural and synthetic anabolic steroids. In popular language, the word "steroids" usually refers to anabolic steroids.
- Cholesterol, which modulates the fluidity of cell membranes and is the principal constituent of the plaques implicated in atherosclerosis.
- Plant
- Phytosterols
- Brassinosteroids
- Fungus
- Ergosterols
Structural
It
is also possible to classify steroids based upon their chemical
composition. One example of how MeSH performs
this classification is available at the
Wikipedia MeSH catalog.
Examples from this classification include:
Class
|
Examples
|
Number of
carbon atoms
|
|---|---|---|
Cholestanes
|
27
|
|
Cholanes
|
24
|
|
21
|
||
19
|
||
18
|
Gonane (or
steroid nucleus) is the parent (17-carbon tetracyclic) hydrocarbon
molecule without any alkyl sidechains.
Source: Wikipedia



2 comments:
nice post and blog.
With so many books and articles coming up to give gateway to make-money-online field and confusing reader even more on the actual way of earning money, buy anadrol australia
Post a Comment